PCOD/PCOS: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also known as polycystic ovarian syndrome, is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. It can cause a range of symptoms due to hormonal imbalances and affects the ovaries’ function. Here’s an overview of PCOS, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment:
Causes:
- Hormonal Imbalance: PCOS is often associated with hormonal imbalances, including higher levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone, and irregularities in insulin production.
- Genetics: There appears to be a genetic component to PCOS, as it tends to run in families.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, can contribute to PCOS by increasing insulin levels, which in turn can stimulate androgen production.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation may also play a role in PCOS development.
Symptoms:
- Irregular Menstrual Periods: Women with PCOS may have irregular, infrequent, or prolonged menstrual cycles.
- Ovulation Problems: PCOS can cause irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation, leading to infertility or difficulty conceiving.
- Excess Androgens: Elevated levels of androgens can cause symptoms such as acne, excess facial or body hair (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic Ovaries: Multiple small cysts may develop on the ovaries, which can be detected via ultrasound.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight.
- Skin Changes: PCOS can lead to skin changes such as darkening of the skin (acanthosis nigricans) and skin tags.
- Mood Changes: Mood swings, depression, and anxiety are common in women with PCOS.
- Sleep Problems: Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, is more prevalent in women with PCOS.
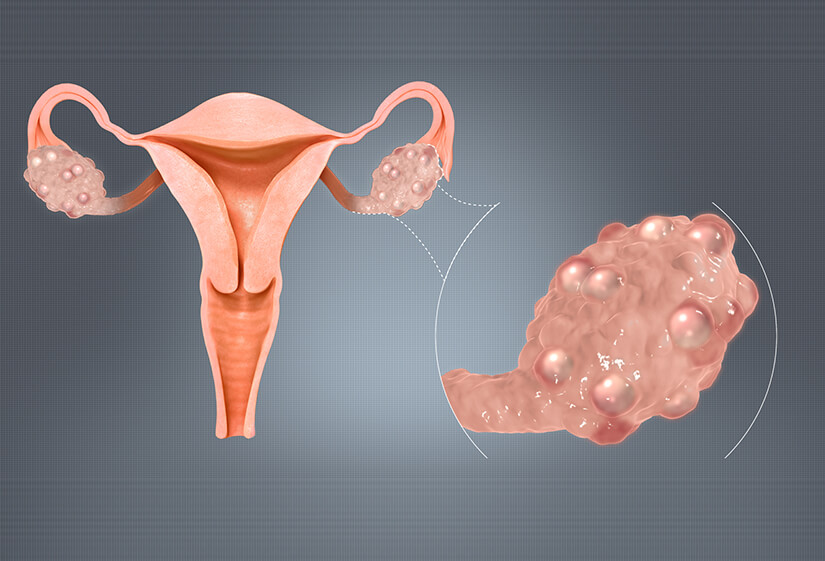
Diagnosis:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will gather a medical history and perform a physical examination to assess symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, and obesity.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure hormone levels, including testosterone, estrogen, and LH (luteinizing hormone), as well as fasting glucose and insulin levels to evaluate for insulin resistance.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the ovaries can detect the presence of multiple small cysts.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Other conditions with similar symptoms, such as thyroid disorders or adrenal gland abnormalities, may need to be ruled out.
Treatment:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management through diet and exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Medications: Hormonal birth control methods, such as oral contraceptives, can regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Anti-androgen medications may also be prescribed to address symptoms like hirsutism and acne. Metformin, a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Fertility Treatments: Women trying to conceive may benefit from fertility medications such as clomiphene or gonadotropins to induce ovulation.
- Management of Symptoms: Treatments for specific symptoms such as acne, hirsutism, and hair loss may include topical medications, laser therapy, or other interventions.
PCOS is a complex condition that may require a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers such as endocrinologists, gynecologists, and nutritionists to address its various aspects effectively.




0 Comments